Soft Tissue Case 4 ED Management
Gout
ED Management
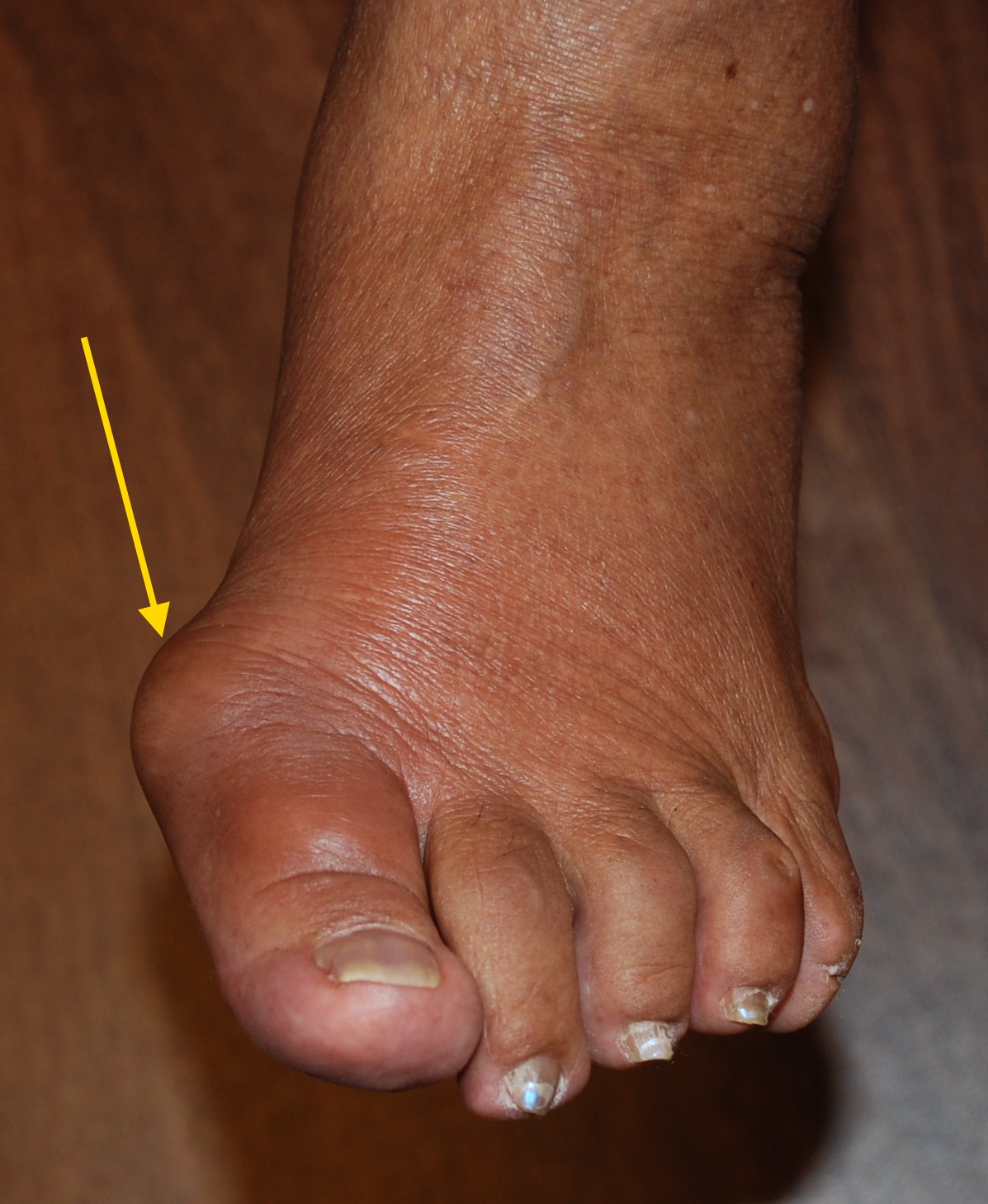
Classic ED treatment options for acute gout have been NSAIDs, COX-2-selective inhibitors, oral or intraarticular corticosteroids, and oral colchicine. Continue chronic prophylactic agents such as probenecid or allopurinol. Encourage RICE treatment.
Relief should begin at 24 hours after NSAID therapy and NSAIDs should be continued for 24 hours after symptoms resolve. Colchicine is dosed at 0.5-0.6mg PO q1-2h until pain is controlled, 3 tabs have been taken within 3 hours, or 10 tablets within 24 hours. GI distress is common and may lead to stopping colchicine before the pain is controlled. Colchicine is less effective after 24 hours and shouldn't be used for another week. Use NSAIDs and colchicine with caution in patients at risk for renal insufficiency. Narcotics may be indicated for acute pain control. Once septic arthritis has been excluded, patients may use a prednisone burst or intraarticular corticosteroid for refractory pain