Soft Tissue Case 4 Background
Gout
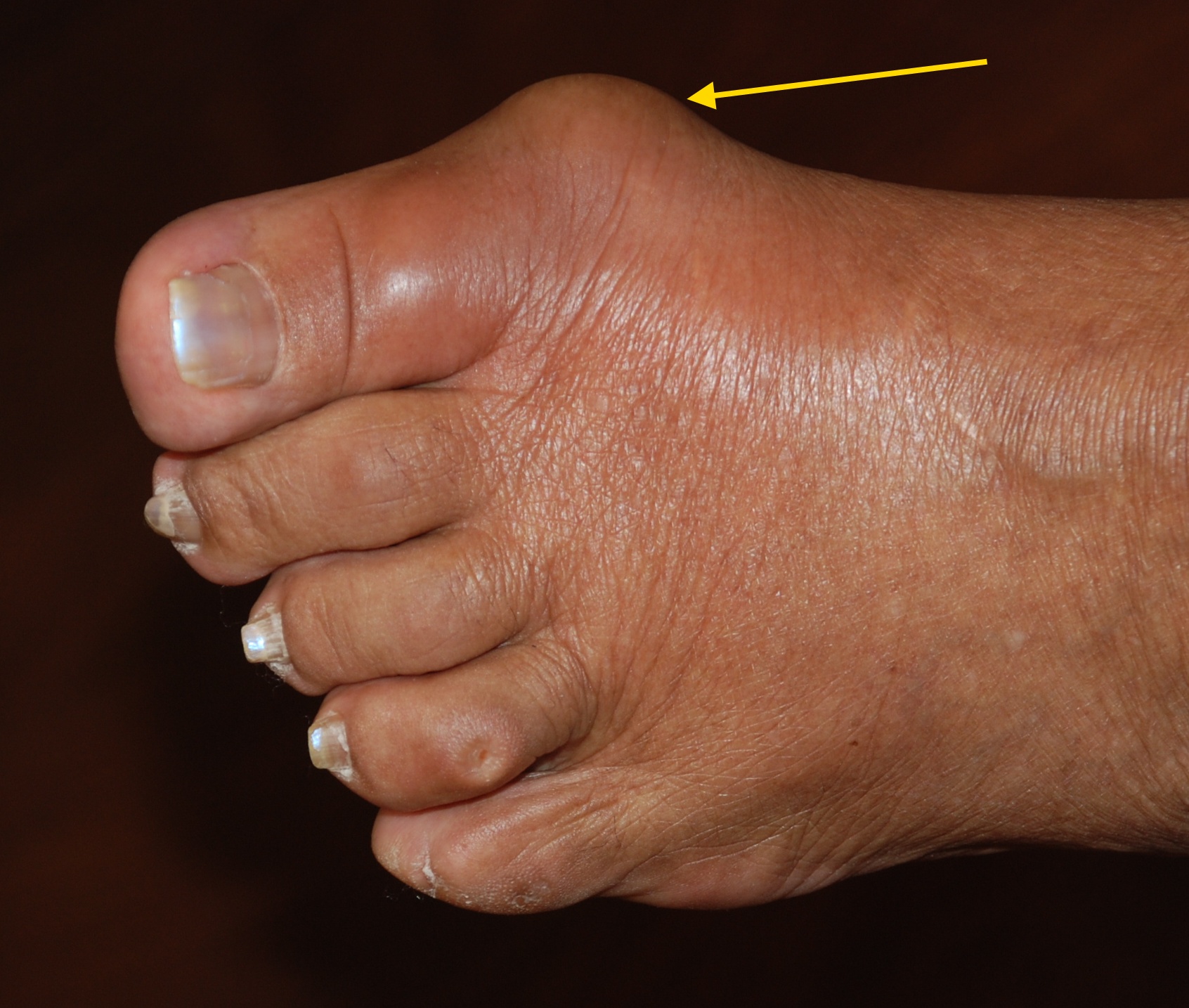
Gout refers to disease in which monosodium urate deposits in joints and soft tissues. Acute gout classically presents in middle-aged men or postmenopausal women often after binges of alcohol or urate-rich diets. It also can also be brought on by stress of illness, trauma or surgery. Thiazide diuretics, antimetabolite medications, myeloproliferative disorders, multiple myeloma, and sickle cell disease have also been associated. 75% of attacks occur about the first MTP joint (podagra). The next most common joints are the knee (godagra), ankle, and tarsal joints. There may be polyarticular involvement, bursitis, tenosynovitis or skin inflammation. Attacks peak at 24-48 hours and resolve within a week. Subsequent attack frequency increases, involving more joints, and may ultimately lead to development of chronic gouty arthritis