Pediatrics Case 14 Background
Salter Harris Type III Fracture of the Proximal Radius
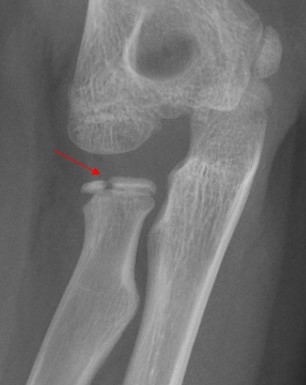
Children commonly sustain injuries of the physis because the cartilaginous growth zone that bridges the physis is weaker than bones and ligaments. The growth plate is the weakest link of the pediatric skeleton. Kids are more likely to fracture through the growth plate than to sprain around it. Be careful diagnosing kids “with just a sprain.”
Salter-Harris classification is used to describe five patterns of physeal injuries. This classification system is helpful because it is a simple way for clinicians to risk stratify these injuries, as lower numbers tend to be less severe and have lower risk of growth-related abnormalities and other feared outcomes. Blood supply to the physis comes from the epiphysis. So fractures that spare the epiphysis, if properly aligned/reduced, are more likely to resume normal bone growth and not develop bone length discrepancy.
Salter III fractures extend through the physis and epiphysis. These are intraarticular fractures. Salter Harris III fractures are relatively uncommon, accounting for approximately 8% of growth plate fractures.