Ankle Case 9 Diagnosis
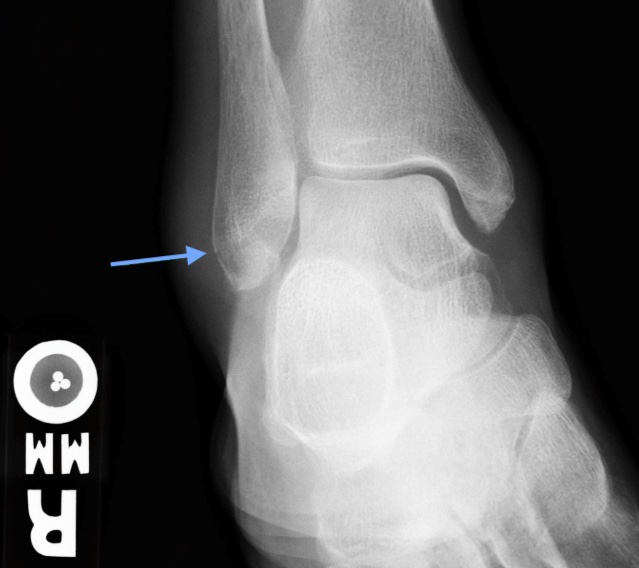
Weber A Fracture
Diagnosis
Standard three-view plain radiograph ankle series should be obtained which includes AP, lateral, and mortise (an AP view shot in 10-20° internal rotation) views. The fibular fracture line should be identified in relation to the ankle mortise. Fractures distal to the mortise are Weber A and are often transverse in orientation.
The joint space should be uniform all around the talus on the mortise view. The “medial clear space” between the medial malleolus and talus should be ≤ 4 mm. Radiographic signs of ankle instability/syndesmotic injury (details of which are beyond the scope of this case) include abnormalities of tibiofibular overlap and tibiofibular clear space.
Stability can be assessed without obtaining CT or MRI. In Weber A fractures, the tibiofibular syndesmosis and deltoid ligament (medially) are intact while the medial malleolus may or may not be fractured. Unless there is a concurrent medial malleolus fracture or medial tenderness on exam, Weber A fractures are stable.