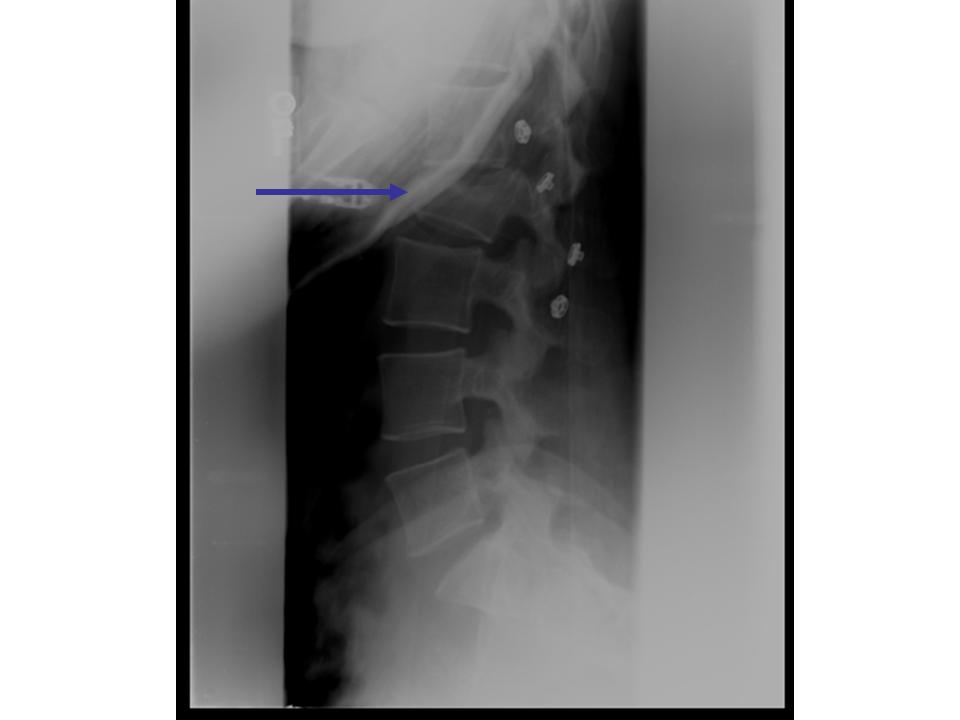
Spine Case 1 Diagnosis
L2 Burst Fracture
Diagnosis
If a fracture is suspicious based on severe pain or neurologic deficits, CT scan is the most appropriate initial study since it is readily available and more sensitive than plain film radiography.
If the diagnosis is by plain films, it is important to distinguish a burst fracture from a simple compression fracture. In a simple compression fracture, the compression should only involve the anterior aspect of the vertebral body. In a burst, the posterior vertebral body is also compressed.
Look for comminution of the posterior-superior corner of vertebral body. Ensure that good quality AP radiographs are done to visualize the posterior elements. Widening of the pedicles on AP films indicate unstable posterior element disruption. CT should be done to assess if there is canal compromise and can better visualize the posterior elements if the plain films suggest a burst fracture. If the posterior elements are disrupted there is >50% association with neurologic injury.